Mako 6.2.0 Release Notes
New and updated features
MAKO-2960 | Vector-based transparency flattenerThis release sees the introduction of a new method to flatten transparency that traces shapes with vector paths rather than rasterising them, avoiding the jagged edges that result. New APIs are added to the IRendererTransform interface:
CPP
CPP
CPP
Example of vector-based flattening 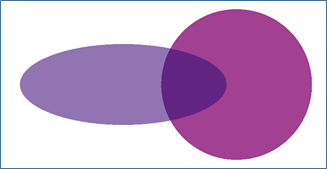 In this example, two partially transparent shapes overlap, and set to use a multiply blend. Zooming in to the top of the area of intersection:  The result of regular raster-based flattening. The shapes are rasterized (at somewhat low resolution for the purposes of illustration) and you can see the jagged edges that result.  The result of vector-based flattening. The edges are smooth. 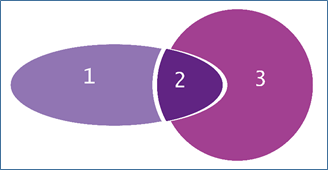 This image shows how the vector flattener has created three new vector paths that no longer overlap (moved apart for the purposes of illustration), with the color of 2 representing the blend evident in the original artwork. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
MAKO-3311 | Enable /CompressObjects with an additional IDistiller() APIAn additional API is added to the IDistiller class to support compressing of individual objects by internally setting the CompressObjects distillerparam. Applies to PDF 1.5 and later. Use Documentation for the SDK samples MakoDistiller and MakoDistillerCmd have been updated accordingly. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
MAKO-3320 | Add equivalent of PDFLib's SetPageFilterRange to IDistiller | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Three new API functions are added to IDistiller to specify which pages in a PostScript job are processed.
Use it in this way. (This code is C++; this API is also available in C# & JAVA).
CPP
Additionally,
CPP
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
MAKO-3350 | IJPDS Performance improvement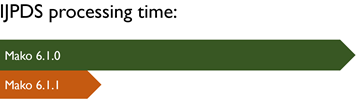 In response to customer requests, the IJPDS input class has undergone significant refactoring that has resulted in an average performance increase of 71%. In particular, the method for obtaining the number of pages now returns almost immediately for most jobs. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
MAKO-335X | IJPDS input class: additional options to control assembly of output pagesThe method to instantiate the class remains the same, but the available parameters have changed.
CPP
This is a complete list of the available parameters. Items marked with an asterisk are new in this version.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
MAKO-3275 | Add support for PDF 1.5 outputThis corrects the omission of PDF 1.5 from the list of supported PDF versions to choose from when using IPDFOutput::setVersion(). See this documentation for details. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
MAKO-3433 | Support CMYK encoding of JPEGUntil this version, saving a Mako IDOMImage or IImageFrame to JPEG meant converting to RGB first. This change adds two additional parameters that permit the encoder to write CMYK data (if available) and whether it should be inverted beforehand. The parameters are:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
MAKO-3249 | Push setFunction() down into IDOMShadingPatternBrushThis change was requested by a developer in Global Graphics’ Technical Services team. The | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
MAKO-3307 | Create VS2017 build of Mako 6.2.0Responding to customer demand, the VS2017 build makes a comeback in this release. x64 only. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Support issues fixed in this release
You will be required to log in to the support portal to follow the MAKOSUP link.
MAKO-3314 | MAKOSUP-10650 Critical MAKO render performanceThe exhibit PDF was very slow to render, taking hours instead of the expected minutes. This job is extremely punishing, consisting of a lot of gradients, particularly radials, with plenty of transparency and overlapping objects. Improving performance for this use case required identifying where the fastest code path for a given process was not being taken, then making the necessary changes to enable those to be used. Additionally, several smaller performance gains, taken together, added to the overall performance improvement.
An anti-aliasing setting of 4 requires a rendering resolution of 900dpi (9 × the data) | ||||||||||||
MAKO-3362 | MAKOSUP-10697 Text incorrectly hidden by redaction | ||||||||||||
While applying redaction to text that happened to be on a non-white background, Mako was losing track of the z-order of objects with the result that adjacent text, not part of the redacted area, was being obscured by the background. This is now fixed. In addition, a new parameter is added to the redactor transform: IRedactorTransform::setGenerateMasks(bool generateMasks) Sets whether masks should be generated when rendering redacted sections. The default is true. Setting this false will result in the text becoming part of the rendered image which may be preferred. The text remains in the DOM, so can still be selected, and searched for. | |||||||||||||
MAKO-3291 | MAKOSUP-10699 Memory usage grows to 10GB then segfaults | ||||||||||||
The exhibit contains a very large clip, most probably the result of an error in the generator of the PDF. It caused scan-conversion at PDF input time to trigger an overflow. There is a straightforward workaround providing such a case is detected, and this is implemented in Mako 6.2.0. With it, the exhibit processes normally and memory usage remains below 30MB. | |||||||||||||
MAKO-3295 | MAKOSUP-10700 Arabic ligature problem | ||||||||||||
The customer’s use case is that they wish to use IDOMGlyphs::getFlattenedGlyphInfo() and see the Arabic ligature in the Unicode information that it returns. Prior to this change, the IDOMGlyph::Data unicodeID would only be populated in this situation if the Unicode was a single code point. Following this change, the IDOMGlyph::Data unicode member now contains the sequence of Unicode codepoints for the ligature, in the form of a UTF32 string, giving the customer what they need. | |||||||||||||
MAKO-3304 | MAKOSUP-10701 An expected PDF object was not found Error | ||||||||||||
This problem surfaced when combining two PDFs. The issue is triggered by several annotations sharing the same AP (appearance) dictionary, which for various reasons was not handled correctly. Now fixed. | |||||||||||||
MAKO-3310 | MAKOSUP-10703 Add the ability for Optional Content to be updated while an IOutputWriter is in progress | ||||||||||||
This change adds a new API - IPDFOutput::setAllowOptionalContentUpdateDuringWrite() (and a corresponding parameter “AllowOptionalContentUpdateDuringWrite”) that will allow Optional Content to be updated while an IOutputWriter is in progress. For this to work, groups being used on a given page must have been added to the optional content before writing that page. Note also:
The API documentation includes these details and more. Enter setAllowOptionalContentUpdateDuringWrite into the Search box | |||||||||||||
MAKO-3309 | MAKOSUP-10706 Support Type 4 (PostScript Calculator) functions for Shading Patterns | ||||||||||||
The exhibit had some unusual shading patterns, in particular a Type 4 pattern in a shade that Mako was unable to handle, eventually causing a segmentation fault during processing. The fix adds full support for Type 4 functions in patterns. | |||||||||||||
MAKO-3346 | MAKOSUP-10712 IFormUnpackerTransform crashes | ||||||||||||
The solution required a workaround for a broken PDF. The exhibit PDF defined a form with a BDC operator for marked content but did not end it with EMC. Mako will now tolerate such a discrepancy. | |||||||||||||
MAKO-3345 | MAKOSUP-10715 Disappearing glyphs | ||||||||||||
This issue was triggered by an unusual font cmap encountered in the exhibit PDF. A fix to Mako’s Format 4 cmap subtable decoding was required. | |||||||||||||
MAKO-3452 | MAKOSUP-10719 PDF to PDF conversion error | ||||||||||||
The exhibit contained a badly formed ICC profile, and this was reported back to the customer. Mako has some protections for bad ICC profiles, but for the exhibit, the problem was the stream itself. Rather than report an error, Mako now falls back to the alternate space, or a device space if no alternate is provided, allowing the job to complete normally. | |||||||||||||
MAKO-3374 | MAKOSUP-10720 File does not succeed in Render | ||||||||||||
This issue was fixed by the work for MAKOSUP-10706: Support Type 4 (PostScript Calculator) functions for Shading Patterns. | |||||||||||||
MAKO-3371 | MAKOSUP-10732 Error Code 2300, error opening input PDF stream | ||||||||||||
The solution required a workaround for a broken PDF. The exhibit PDF defined a /Info dictionary with a /Title string that had a unescaped '(' in the middle of the string. Mako will now tolerate such an occurrence but is not able to recover the document properties. | |||||||||||||
MAKO-3382 | MAKOSUP-10733 Thumbnail SIGSEGV | ||||||||||||
When rendering the exhibit PDF at low resolution, a segmentation fault is thrown. Now fixed. | |||||||||||||
MAKO-3420 | MAKOSUP-10736 SIGKILL / High memory issue | ||||||||||||
The combination of Metadata streams in excess of 8 megabytes present in the exhibit, plus an error in code concerned with allocating memory, caused Mako to throw an out-of-memory exception. A simple fix solved the problem and keeps memory consumption below 2GB. | |||||||||||||
MAKO-3425 | MAKOSUP-10749 Exception while loading specific pdf | ||||||||||||
Pre-flight checks warn of font and syntax errors that the exhibit presents with, and Mako failed with a CID font substitution error. A solution was found. Now fixed. |
Other issues
MAKO-1942 | Mako signals undefined error for 12_14K.PSAn obscure error when rendering Type 1 Shading Patterns is now fixed. |
MAKO-2450 | Character stroke overprinting not being retainedThe exhibit features white text on a colored background, with a black stroke which was not overprinting correctly. Now fixed. |
MAKO-2454 | Backgrounds of graphs wrong when converting PDF to PDFThe exhibit features graphs that lost color information during processing. Now fixed. |
MAKO-2568 | CMAP test fails when processing 409-01.PS with makodistillerThe exhibit features specific PostScript tests, one of which is designed to test a CMap (PostScript Level 3 Character code mapping). It now passes. |
MAKO-3250 | Investigate why imposition output is larger in 6.1.0 than 6.0.1Processing to produce large imposition signatures produced PDFs whose size unexpectedly grew in Mako 6.1.0. Investigation showed this was due to an improvement made to retain XMP metadata associated with images that interfered with the hashing mechanism thereof, reducing the opportunity to cache repeated images. This has now been addressed, and further improved by also enabling caching of XMP packets, bringing file sizes back down to below those seen in Mako 6.0.1. |
MAKO-3256 … MAKO-3261MAKO-3298 | Memory leak issuesAs part of an ongoing effort to track down and fix memory leak issues, these stories were completed during the Mako 6.2.0 development cycle. |
MAKO-3283 | Transparency blending is not processed correctly with alphaGeneration featureMako 6.1.0 introduced a new option generate an alpha channel when rendering page content. During testing an example was found where this option interfered with regular transparency blending. Now fixed. |
MAKO-3284 | Issue triggered by recent clipping changesMako 6.1.0 introduced improvements to object clipping behavior but these were later found to have some undesirable, albeit minor, side effects. Now addressed. |
MAKO-3287 | Fonts in MakoDistillerCMD output differ from PDFLib and Acrobat DistillerIt was noted during testing that the different PostScript to PDF conversion routes were producing different output, even though the same underlying code was in use in all three. This led to some lengthy investigation and subsequent refactoring of font handling logic to eliminate discrepancies and produce correct output from the IDistiller class. |
MAKO-3319 | Ensure that complex gstate parameters are applied for stroked char path groupsThis was discovered when comparing rendered output from before and after PDF-to-PDF processing by Mako. Although the visual improvements are very small (typically a few pixels difference), our aim for Mako is zero visual differences between an input and an output PDF, where no deliberate changes are made. |
MAKO-3323 | PDF Output: Incorrect UCR function written for PostScript Calculators with a DomainFound during routine testing. Now fixed. |
MAKO-3324 | Fix LAB color space range handling for PDF outputFound during routine testing. In some circumstances Mako was not emitting the correct LAB Range entries from the source space. Now fixed. |
MAKO-3325 | Correct a UserUnit pattern matrix issue causing patterns to be incorrectly placedFound during routine testing. Incorrect scaling of an element occurred due to the UserUnit scaling value not being correctly considered. Now fixed. |
MAKO-3327 | Implement Type 3 render mode semantics for PDF 2.0Found during routine testing. Two jobs were not rendering as they should. Further examination showed rendering modes not being honoured for text using Type 3 fonts. However, both were PDF 2.0, the specification for which updates text rendering mode requirements. Once the necessary changes were made, the jobs rendered correctly. |
MAKO-3336 | PDF front-end truncating CID font widths informationWhen converted PDF-to-PDF with Mako, the job exhibited shifts in glyph position when the input and output were compared. One solution for this is to round rather than truncate the values in question, but the one adopted was simpler and more accurate: switch to using floating-point values rather than integers. |
MAKO-3337 | Default color spaces not being applied to inline imagesFound during routine testing. Following PDF-to-PDF processing, inline images on a page exhibited a color shift. The fix required refactoring of core code to deal with default color spaces, ensuring special color spaces (e.g., Indexed, Separation, DeviceN and Pattern) which can have an underlying device space are handled correctly. |
MAKO-3339 | Characters appearing where notdefs should be for PDF to PDFFound during routine testing. The exhibit was unusual as it used a font type that did not specify an encoding, and the encoding to which Mako defaulted was the wrong choice, leading to a character that should have displayed as a notdef, instead displayed as a glyph. Now fixed. |
MAKO-3367 | Improve text knockout handlingFound during routine testing of a PDF 2.0 test suite designed to exercise these document features. When converting PDF-to-PDF, text was not knocked out correctly. Now fixed. |
MAKO-3380 | Fix an issue triggered by the fix of MAKO-3304 (IA2_2106.PDF)Found during routine testing. The change for MAKO-3304 caused this job to crash. The job is bad: one of the Form XObjects used as an annotation appearance is a dictionary and not a stream(!) This is not allowed, but Mako didn’t cope with the breakage. Now fixed. |
MAKO-3388 | Rendering some jobs to CMYK results in disappearing textFound during routine testing. A problem caused by incomplete detection of opaque text resulted in text being dropped from rendered output. Now fixed. |
MAKO-3389 | Floating point CFF parameters rounded by JawsFound during routine testing of PDF-to-PDF conversion. Fonts of the CFF (Compact Font Format) variety were not retaining their scaling parameters correctly, leading to small variations in height and width. Now fixed. |
MAKO-3407 | Patterns applied to Type 3 text not scaled correctlyNow fixed. |
MAKO-3431 | Correctly clip and scale ICC LAB colour values in Mako PDF inputFor ICC colour spaces, Mako was simply clamping all input values to the range 0 to 1. For LAB profiles however, the PDF specification specifies L 0<->100, A -128<->127 and B -128<->127. Now fixed. |
Distribution
MAKO Version 6.2.0 is built for the following platforms:
iOS
macOS
Linux (for Debian-based distributions, eg Ubuntu, Mint)
Linux (Centos)
Linux (for Debian Buster) (ARM32 for Raspberry Pi)
Linux (for Debian Stretch)
Linux (for MUSL distributions, eg Alpine Linux)
Linux (for Ubuntu 20.04 LTS)
Windows (static and dynamic libs, VS 2019 (V142), x86 and x64)
Windows (static and dynamic libs, VS 2017 (V141), x64)
Windows UWP (Store apps, Windows 10 IoT)
Note that the Android build has been dropped from this release pending a tooling change. Please contact Mako support if you need a Mako release for Android later than Mako 6.1.0.
Mako supports the following programming languages
C++ (Mako is written in C++)
C# (.Net Framework and .Net Core)
Java (built with OpenJDK11)
Python (v3.8)
The alternatives to C++ are built using SWIG (www.swig.org) which provides a translation to the native libraries, found in these distribution folders:
Linux_SWIG_(C#-Java-Python)
Linux_Ubuntu_SWIG_(C#-Java-Python)
macOS_SWIG_(C#-Java-Python)
Windows_SWIG_(C#-Java-Python)
