(v13) VTune general microarchitecture analysis
This page applies to Harlequin v13.1r0 and later; and to Harlequin Core but not Harlequin MultiRIP
This showed immediately that the RIP is primarily memory bound and core bound, at least when processing representative graphic arts and primary packaging jobs.
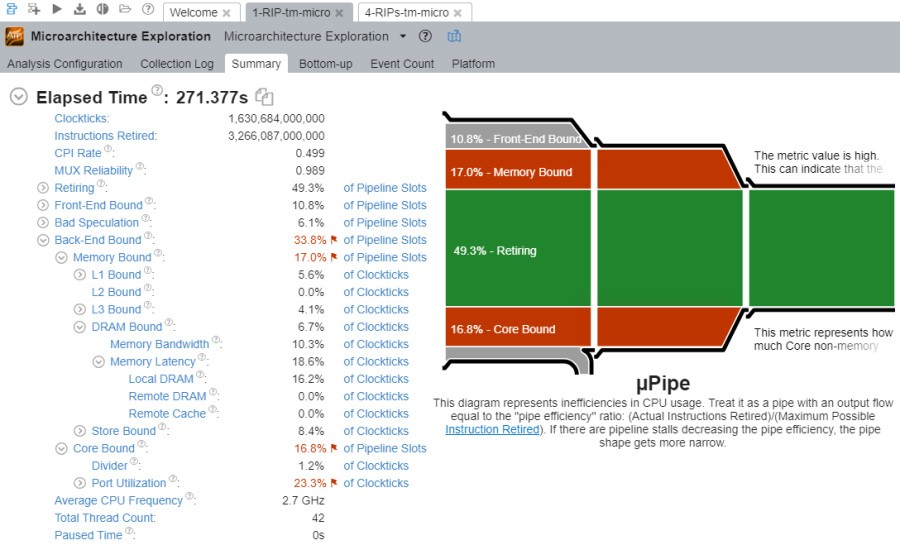
Figure: VTune general microarchitecture analysis: One RIP - band height 32; four render threads
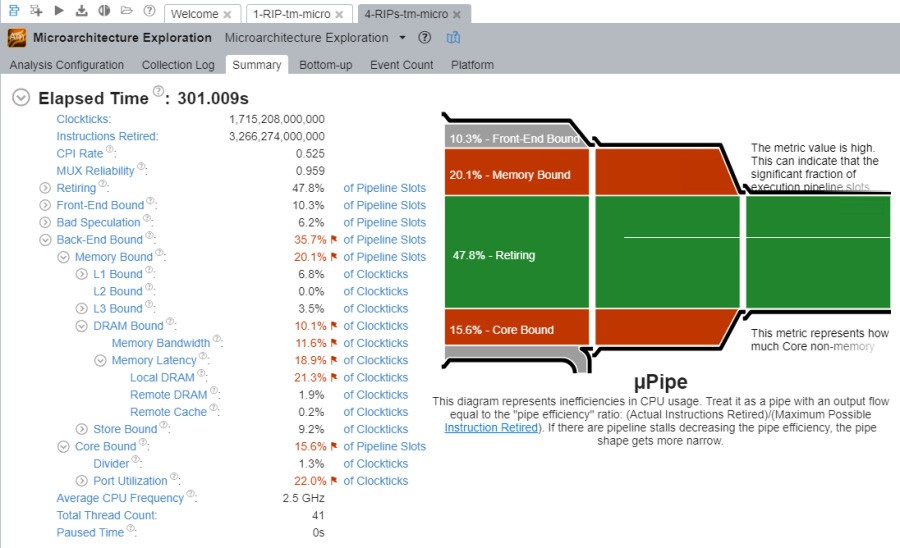
Figure: VTune general microarchitecture analysis: Four RIPs - band height 32; four render threads
In Figure: VTune general microarchitecture analysis: Four RIPs - band height 32; four render threads , the most obvious difference is that, when four RIPs are being used, the memory bound percentage goes up. This therefore merits a closer look.
The core bound figure is actually slightly less for four RIPs compared to one RIP, but we suspect this could simply be random deviation, or because processing is waiting for transfers to and from memory.
